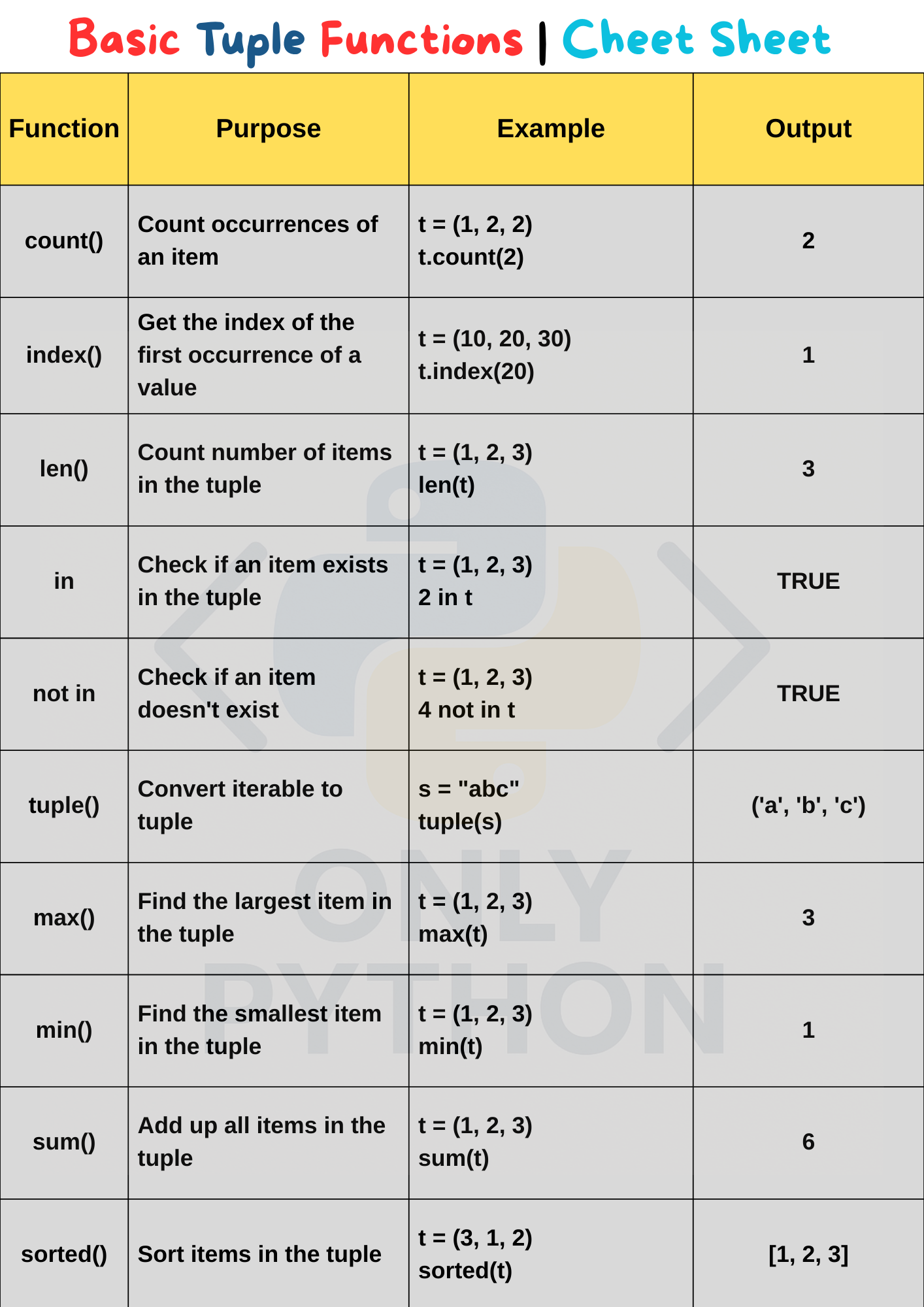
Python Basic Tuple Functions Cheat Sheet with Examples
1. count() Function
The count() function returns the number of times a specified value appears in the tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 5)
print(my_tuple.count(2))
Output:
3
2. index() Function
The index() function returns the first index of the specified value in the tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = ('a', 'b', 'c', 'a', 'd')
print(my_tuple.index('a'))
Output:
0
⚠️ If the value is not found, it raises a ValueError:
# my_tuple.index('x') → ValueError
3. len() Function
The len() function returns the number of elements in a tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = (10, 20, 30, 40)
print(len(my_tuple))
Output:
4
4. in Keyword
The in keyword checks if a value exists in a tuple. Returns True or False.
Example:
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4)
print(3 in my_tuple)
print(10 in my_tuple)
Output:
True
False
5. not in Keyword
The not in keyword checks if a value does not exist in a tuple. Returns True or False.
Example:
my_tuple = ('apple', 'banana', 'cherry')
print('orange' not in my_tuple)
print('banana' not in my_tuple)
Output:
True
False
6. tuple() Function
The tuple() function converts other data types (like lists, strings) into a tuple.
Example 1: Convert list to tuple
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
my_tuple = tuple(my_list)
print(my_tuple)
Output:
(1, 2, 3)
Example 2: Convert string to tuple
text = "hello"
print(tuple(text))
Output:
('h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o')
7. max() Function
The max() function returns the largest element in the tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = (5, 10, 25, 3)
print(max(my_tuple))
Output:
25
8. min() Function
The min() function returns the smallest element in the tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = (5, 10, 25, 3)
print(min(my_tuple))
Output:
3
9. sum() Function
The sum() function returns the total sum of all elements in the tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4)
print(sum(my_tuple))
Output:
10
10. sorted() Function
The sorted() function returns a new sorted list from the tuple, leaving the original tuple unchanged.
Example:
my_tuple = (4, 1, 3, 2)
sorted_list = sorted(my_tuple)
print(sorted_list)
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
✅ Convert back to tuple:
sorted_tuple = tuple(sorted(my_tuple))
print(sorted_tuple)
Output:
(1, 2, 3, 4)
📚 Related Topics:
- ➤ Python Arithmetic Operators
- ➤ Basic String Functions
- ➤ Advanced String Functions
- ➤ Basic List Functions
- ➤ Advanced List Functions : Part-1
- ➤ Advanced List Functions : Part-2
- ➤ Basic Tuple Functions
- ➤ Advanced Tuple Functions
- ➤ Basic Dictionary Functions
- ➤ Advanced Dictionary Functions
- ➤ Conditional Statements : if-elif-else
- ➤ Python 'for' Loop
- ➤ Python 'while' Loop
- ➤ Difference between 'for' loop and 'while' loop
- ➤ Introducing Python Functions
📌 Bookmark this blog or follow for updates!
👍 Liked this post? Share it with friends or leave a comment below!