Python: Advanced String Functions Cheat Sheet with Examples
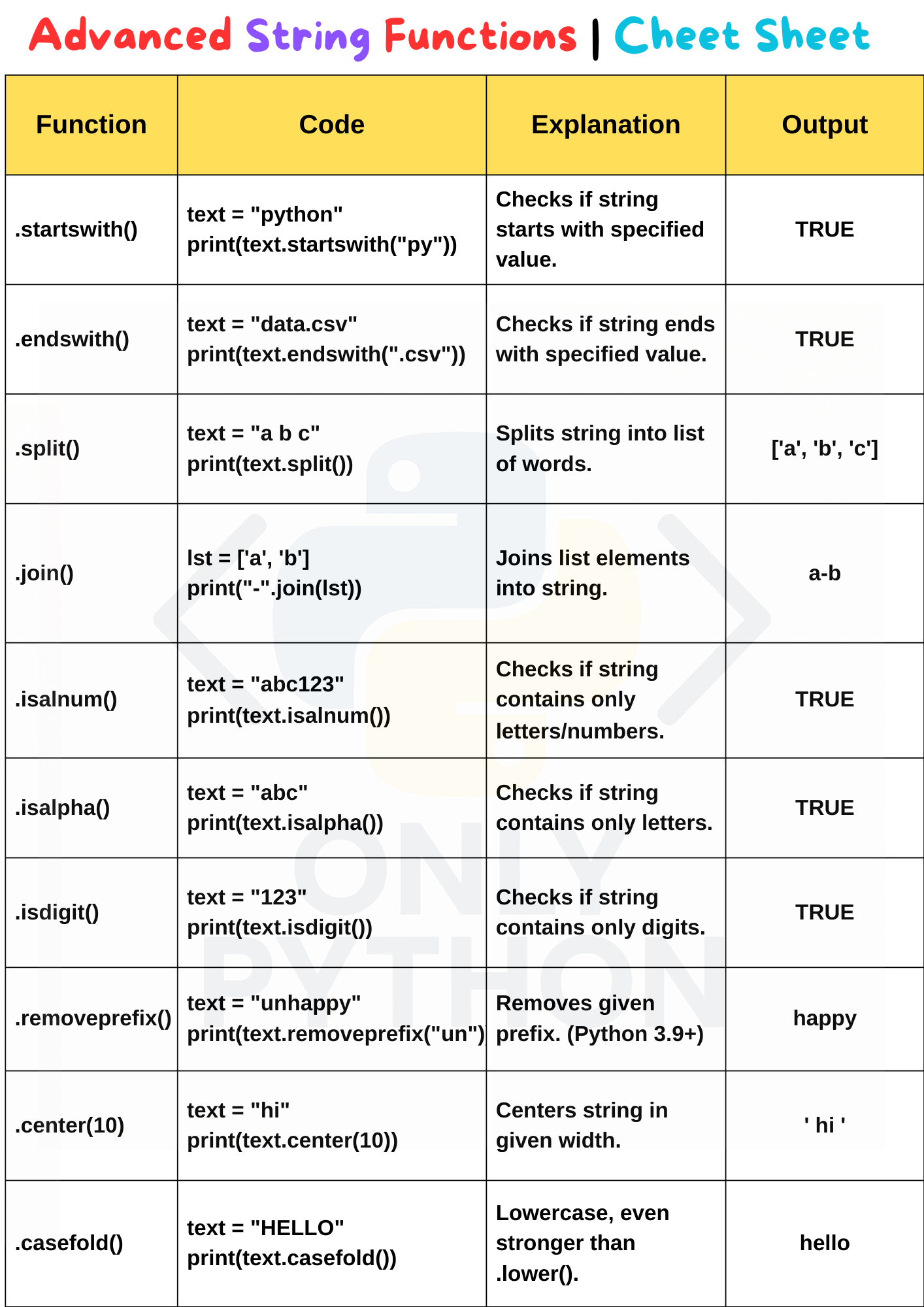
1. startswith() Function
The startswith() function returns True if a string starts with the specified substring, else False.
Example 1:
text = "Python is fun"
print(text.startswith("Python"))
Output:
True
⚠️ Point to Remember:
text = "python is fun"
print(text.startswith("Python")) # Case sensitive
Output:
False
2. endswith() Function
The endswith() function returns True if the string ends with the specified substring, else False.
Example 1:
text = "Learn Python"
print(text.endswith("Python"))
Output:
True
⚠️ Point to Remember:
text = "Learn Python Programming"
print(text.endswith("Python"))
Output:
False
3. split() Function
The split() function breaks a string into a list using a separator (default is space).
Example 1:
text = "apple banana mango"
print(text.split())
Output:
['apple', 'banana', 'mango']
Example 2 (Custom Separator):
data = "12,34,56"
print(data.split(","))
Output:
['12', '34', '56']
4. join() Function
The join() function joins the elements of a list into a single string with a specified separator.
Example 1:
words = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
print("-".join(words))
Output:
apple-banana-cherry
✅ Special Use Case:
Joining characters in a string:
text = "abc"
print(",".join(text))
Output:
a,b,c
5. isalnum() Function
The isalnum() function returns True if all characters in a string are alphanumeric (A-Z, a-z, 0-9), with no spaces or symbols.
Example 1:
print("abc123".isalnum())
Output:
True
Example 2 (With Symbol):
print("abc@123".isalnum())
Output:
False
⚠️ Point to Remember:
Spaces are not alphanumeric:
print("abc 123".isalnum())
Output:
False
6. isalpha() Function
The isalpha() function returns True if all characters in a string are alphabets (A–Z or a–z) and there are no digits, spaces, or special characters.
Example 1:
text = "Python"
print(text.isalpha())
Output:
True
Example 2 (with space):
text = "Python Code"
print(text.isalpha())
Output:
False
⚠️ Point to Remember:
Even spaces and numbers will make it return False.
7. isdigit() Function
The isdigit() function returns True if all characters in a string are digits (0–9).
Example 1:
num = "123456"
print(num.isdigit())
Output:
True
Example 2 (with space):
num = "123 456"
print(num.isdigit())
Output:
False
8. removeprefix() Function
The removeprefix() function removes the specified prefix from the beginning of the string, if it exists. This method was introduced in Python 3.9.
Example 1:
text = "unwantedText"
print(text.removeprefix("un"))
Output:
wantedText
Example 2 (prefix not present):
text = "hello"
print(text.removeprefix("un"))
Output:
hello
⚠️ Point to Remember:
This method does not affect the string if the prefix is not found.
9. center() Function
The center() function returns a new string of a specified width with the original string centered and padded with a fill character (default is space).
Example 1:
text = "Python"
print(text.center(20))
Output:
Python
Example 2 (using * as fill character):
text = "Python"
print(text.center(20, "*"))
Output:
*******Python*******
⚠️ Point to Remember:
If the specified width is less than the string length, it returns the original string.
10. casefold() Function
The casefold() function is similar to lower() but is more aggressive. It is used for **case-insensitive comparisons**, especially in different languages.
Example 1:
text = "PYTHON"
print(text.casefold())
Output:
python
Example 2 (for comparison):
str1 = "Straße"
str2 = "STRASSE"
print(str1.casefold() == str2.casefold())
Output:
True
✅ Special Use Case:
casefold() is ideal for comparing strings in **Unicode**, like German "ß".
📚 Practice Questions:
📚 Related Topics:
- ➤ Python Arithmetic Operators
- ➤ Basic String Functions
- ➤ Advanced String Functions
- ➤ Basic List Functions
- ➤ Advanced List Functions : Part-1
- ➤ Advanced List Functions : Part-2
- ➤ Basic Tuple Functions
- ➤ Advanced Tuple Functions
- ➤ Basic Dictionary Functions
- ➤ Advanced Dictionary Functions
- ➤ Conditional Statements : if-elif-else
- ➤ Python 'for' Loop
- ➤ Python 'while' Loop
- ➤ Difference between 'for' loop and 'while' loop
- ➤ Introducing Python Functions
📌 Bookmark this blog or follow for updates!
👍 Liked this post? Share it with friends or leave a comment below!